- TOP
- List of reports
- Anti-Tumor Activity Expressed through Immunopotentiation by a Mixture of Agaricus blazei Murrill and
Chlorella Extracts
Anti-Tumor Activity Expressed through Immunopotentiation by a Mixture of Agaricus blazei Murrill and Chlorella Extracts
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Anti-Tumor Activity Expressed through Immunopotentiation by a Mixture of Agaricus blazei Murrill and Chlorella Extracts
Published in Medicine and Biology
- Objectives
- Agaricus blazei Murrill and Chlorella have been reported to enhance immune function and thus exert anti-tumor activity. The mechanism for such action involves many unresolved questions. The present study in mice was conducted to elucidate part of such a mechanism.
- Methods
- Tumor cells-implanted mice were divided into the control group and the ABM-C group (receiving a mixture of Agaricus blazei Murrill and Chlorella extracts). The tumor burden, cytokines1), NK cell activity2), CTL activity3) and flow cytometry analysis4) of blood were analyzed.
- Results
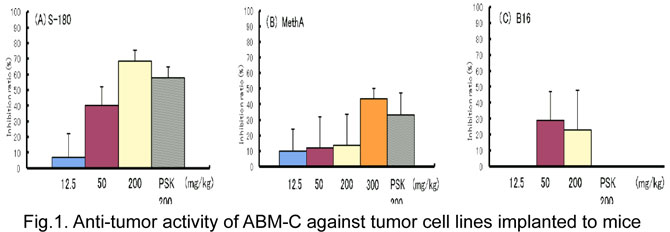
- Proliferation of two tumor cell lines, i.e., sarcoma cell (S-180) and fibroblastic sarcoma cell (Meth-A), was significantly suppressed. Malignant melanoma cells (B16) tended to be suppressed but this change was not significant (Fig. 1).
- On the basis of the above results, we concluded that chlorella ingestion attenuated immunological depression during participation in a sports training camp.
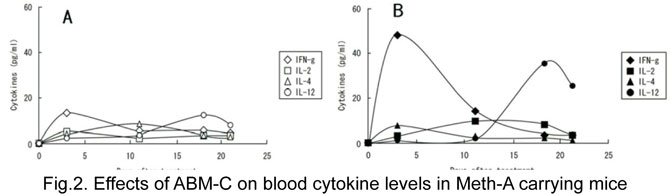
- In analysis of cytokines, IFN-γ increased 3 days after tumor cell implantation and IL-1 increased 18 days after implantation (Fig. 2A). In mice treated with ABM-C after tumor implantation, IFN-γ and IL-12 increased markedly 3 and 18 days after implantation, respectively (Fig. 2B).
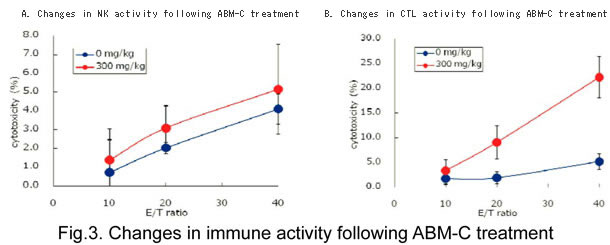
- In analysis of NK cell activity, the splenocytes had higher NK activity in the ABM-C treatment group than in the control group, although this difference was not significant (Fig. 3A). CTL activity was significantly increased by ABM-C treatment (Fig. 3B).
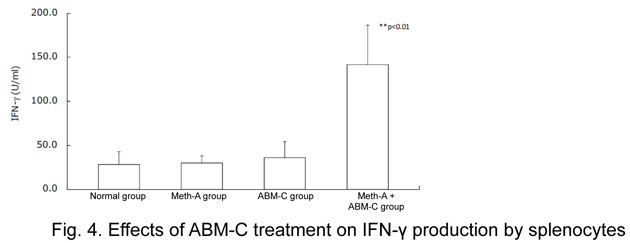
- INF-γ production by the splenocytes removed from the group receiving ABM-C treatment after Meth-A implantation was about 4 times larger than in the other groups (Fig 4).
- In flow cytometry analysis , the percentage of mature type macrophages
(Cass II expressed cells) in peripheral blood was significantly higher following
ABM-C treatment.
These results suggest that ABM-C exerts anti-tumor activity and that not only CTL activation but also macrophage activation plays an important role in the mechanism for this action of ABM-C.
Terminology
- 1)Cytokine
- Low-molecular-weight protein produced by cells in response to stimuli. Binding of cytokine to the receptor on other cells leads to activation, differentiation and proliferation of the cells.
- 2)NK cell (natural killer) cell
- A type of lymphocyte which attacks and eliminates pathologic cells non-specifically. This cell plays an important role in the early stage of infection.
- 3)CTL (cytotoxic T cell, killer T cell)
- A cell which specifically recognizes one's own somatic cells which have become pathologic, attempting to attack and eliminate such cells. CTL is diverse and possess high recognizing function.
- 4)Flow cytometer
- A device capable of distinguishing among immunocytes which have different functions although looking similar to each other. This study used a flow cytometer for analysis of mononucleated cells (macrophages).
Details
- Journal:
- Medicine and Biology Vol.156 No.1 (2012) 26-34
- Title:
- Anti-Tumor Activity Expressed through Immunopotentiation by a Mixture of Agaricus blazei Murrill and Chlorella Extracts
- Authors:
- Yukari Arakawa1), Masaki Fujishima1), Tohru Mizoguchi1), Masahiko Hayashi2)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Sun Chlorella Corporation, 2) Kitasato Institute (currently: Department of Pharmacy, Iwaki Meisai University)





