- TOP
- List of reports
- Effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorella) in Preventing Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Disorders
Effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorella) in Preventing Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Disorders
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorella) in Preventing Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Disorders
Published in Medicine and Biology Vol. 156 No. 10
- Objectives
- Radiation is a useful tool for anti-cancer chemotherapy but it affects not only cancer cells
but also normal cells, possibly resulting in anemia, leukopenia (due to lymphopenia),
reduced production of hematopoietic cells (thrombopenia, etc.) and so on and exerting
unfavorable impacts on immune function, as known since many years ago. Recently,
contamination by radiation released by atomic power plant accidents has also been
highlighted as a serious social problem.
Chlorella is rich in protein and contains polyunsaturated fatty acids (known to be abundantly contained in tuna fish), edible fibers (comparable to those in barley) and a variety of vitamins (folate needed for maintenance of homeostasis, vitamin B12, etc.), minerals and essential amino acids in a well-balanced manner. In addition, Chlorella has been studied as a substance exerting diverse physiological actions.
The present study was conducted to evaluate the effects of Chlorella in reducing the unfavorable influence of radiation on the basis of hematological test, histological examination of immune system (spleen and thymus), etc.
- Methods
- The study used SPF1) ICR/Slc male mice (purchased from Japan SLC, Inc. Hamamatsu City). The immune system of these mice was normal upon purchase but it became compromised following exposure to radiation at the experimental facility. The radiation level was set at 5.0 Gy on the basis of the preliminary test results. The normal mice and the mice with radiation-induced compromised immune function received either Chlorella (the Chlorella group) or physiological saline alone (the saline group) for 10 days (the observation period) beginning 24 hours after exposure to radiation. For precise measurement of the Chlorella dose level, Chlorella (1 g/kg body weight) was suspended in physiological saline and this suspension was orally administered. Hematological parameters and findings from histological examination of spleen and thymus (organs serving as the immune system command center) were compared. During the observation period, all mice received food and water ad libitum.
- Results
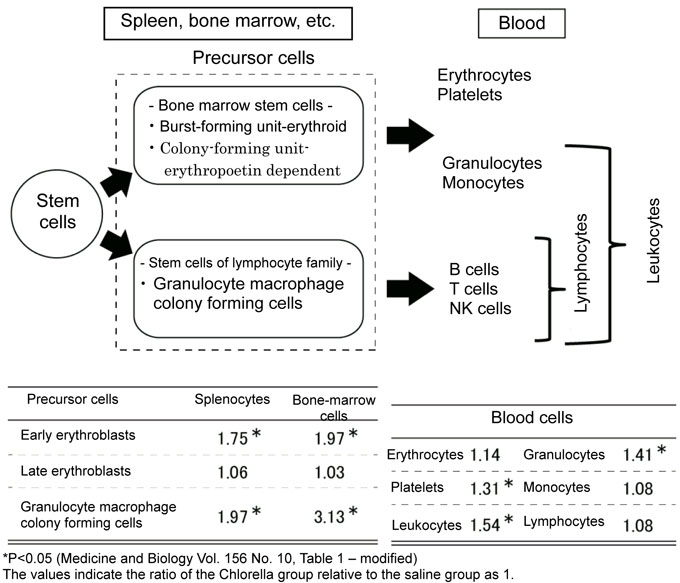
- Fig. 1 graphically represents the results of hematological test and histological examination for mice with radiation-induced compromised immune function as well as differentiation of the cells tested2). The values shown here indicate the ratio of the Chlorella group relative to the saline group as 1. The Chlorella group showed significant increase of leukocytes, granulocytes and platelets known to play important roles in immediate immune defenses. Erythrocytes (serving as oxygen transporter) and monocytes and lymphocytes (important in immune function) showed only slight increase, but the erythrocyte precursors and granulocyte macrophage colony forming cells (which are sources for formation of these cells) significantly increased. Although detailed data are not shown here, the Chlorella group showed significant increase in all of the weight of spleen/thymus (the immune system command center) and the antibody forming potential. Although these cells decreased in the mice with compromised immune function given Chlorella or saline, the study-report 2 magnitude of decrease was smaller following Chlorella treatment. Radiation is known to reduce the hematopoietic cell count as well as the cell count, weight and antibody forming potential of spleen and thymus. In the present study, however, treatment with Chlorella resulted in significant increase of leukocytes, granulocytes and platelets (playing important roles in immediate immune defense against foreign body) and significant increase of erythrocyte precursors and granulocyte macrophage colony forming cells (sources for formation of erythrocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes). These results suggest the possibility of Chlorella to provide a useful means of stimulating recovery from hematopoietic disorders, bone marrow dysfunction, compromised antibody formation and immune responses and so on caused by radiation or anti-cancer chemotherapy and to facilitate resistance of the host to immune dysfunction.
Terminology
- 1) SPF
- Animals free of specific pathogens (microorganisms and parasites)
- 2) Differentiation
- Differentiation: Maturation of stem cells into cells with specific function
Details
- Professional:
society meeting - Medicine and Biology Vol.156 No.1 (2012) 696-702
- Title:
- Effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorella) in Preventing Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Disorders
- Authors:
- Hiroko Ito1), Masaki Fujishima2), Yukari Arakawa2), Fuka Nakata3), Hitoshi Ito4)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Department of Marine Biology and Chemistry, Faculty of Bioresources, Mie University, 2) Sun Chlorella Corporation, 3) Power Full Health Foods Corporation, 4) Microbial Pharmacology Institute





