- TOP
- List of reports
- Effect of Chlorella pyrenoidosa on fecal excretion and liver accumulation of polychlorinated
dibenzo- p -dioxin in mice
Effect of Chlorella pyrenoidosa on fecal excretion and liver accumulation of polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxin in mice
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Effect of Chlorella pyrenoidosa on fecal excretion and liver accumulation of polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxin in mice
- Method
- This test was examined on fecal excretion and liver accumulation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin in mice administered dioxin and fed a 10% Chlorella pyrenoidosa in their diet. This test was also compared using Spinach (dry powder) in their food.
- Results
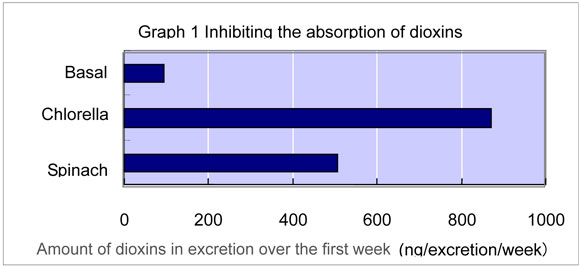
- a. The amount of dioxins in excretion after one week (Graph 1)
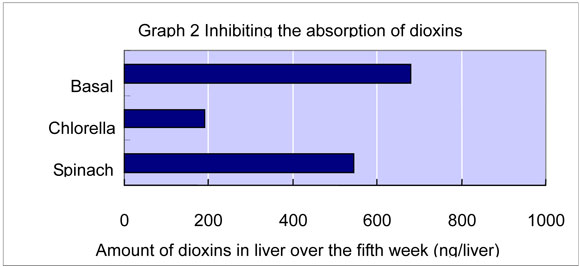
The 10% Chlorella pyrenoidosa diet group excreted dioxins approximately 9.2 times than mice fed the basal diet. The Spinach diet group excreted dioxins approximately 5.3 times than mice fed the basal diet. Mice fed the 10% Chlorella pyrenoidosa diet excreted dioxin almost double than mice fed Spinach diet. - b. The amount of dioxins in liver after five weeks (Graph 2)
Liver accumulation in mice fed the 10% Chlorella pyrenoidosa diet was significantly less by 27.9% than that observed among mice fed either the basal diet and the Spinach diet by 34.8%.
On the other hand, it didn't show significant difference between mice fed the Spinach diet and mice fed the basal diet. - These findings show that Chlorella may be useful in inhibiting the absorption of dioxins through food and the reabsorption of dioxins stored already in the body. It also shows that Chlorella prenoidosa has much more promoting effect to eliminate dioxins than green and yellow vegetables as spinach.
Presentation at a scientific meeting
- Listed Magazine:
- "CHEMOSPHERE" (Volume 59, Number 2, April, 2005)
- Publisher:
- ELSEVIER (Amsterdam, Netherlands)
- Title:
- Effect of Chlorella pyrenoidosa on fecal excretion and liver accumulation of polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxin in mice





