- TOP
- List of reports
- Study of peptidoheteroglycans prepared from Chlorella
Study of peptidoheteroglycans prepared from Chlorella
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Study of peptidoheteroglycans prepared from Chlorella
Published in NIPPON SUISAN GAKKAISHI Vol. 81, No. 2, pp. 267-273 (2015)
- Study objectives
- During the initial stage of infection with foreign matter such as pathogens, complements are activated, resulting in the stimulation of immune cells such as macrophages and NK cells and rapid elimination of the foreign matter. There are two complement activation pathways: one involving innate immunity that responds quickly and the other involving acquired immunity that requires preparation for response. The polysaccharide "β-(1-6)-D-glucan protein complex" that is present in Agaricus blazei Murill and exhibits antitumor activity is known to activate complement. Preliminary studies have indicated that Chlorella also contains a substance activating complements. Thus, as a next step, we analyzed the composition of the polysaccharide prepared from Chlorella and examined the activation of complement and macrophages by oral administration of the polysaccharide.
- Study method
- We analyzed the composition of the polysaccharide by evaluating the presence of carbohydrate, proteins, and amino acids. In addition, we investigated the pathway of complement activation in human serum as well as measured the activation of complements and macrophages in mice after oral administration of the polysaccharide for 1 week to evaluate the effects on the immune system.
- Results
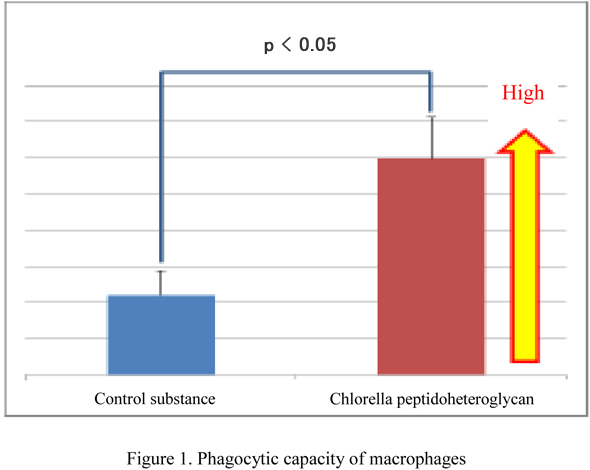
- The results revealed that the polysaccharide of Chlorella that activates complements was a peptidoheteroglycan rich in acidic amino acids, containing 70.3% carbohydrate and 29.5% proteins. The polysaccharide was also shown to quickly activate complements utilizing innate immunity in human serum. Furthermore, the immune system was stimulated by activation of complements in the mouse experiment, resulting in an increase in activated macrophages and enhancement of the ability to eliminate foreign matter from the body (phagocytic capacity) (Figure 1).
- The above results showed that the polysaccharide present in Chlorella was a peptidoheteroglycan, which demonstrated the ability to quickly eliminate foreign matter from the body after oral consumption. We suggest that the peptidoheteroglycan present in Chlorella can be useful in adjuvant immunochemotherapy through advancement of research on its properties in future.
Details
- Journal:
- NIPPON SUISAN GAKKAISHI Vol. 81, No. 2, pp. 267-273 (2015)
- Title:
- Effects of a peptidoheteroglycan prepared from Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorophyceae) on complement C3 and peritoneal macrophages
- Authors:
- Hiroko Ito1,4, Makoto Kakinuma1, Masaki Fujishima2, Yukari Arakawa2, Fukuyoshi Nakata3, Hitoshi Ito4
- Affiliation:
- 1) Laboratory of Marine Biochemistry, Faculty of Bioresources, Mie University,2) Sun Chlorella Corp., 3) Powerful Health Foods Corporation, 4) Research Institute of Mycology and Pharmacology





