- TOP
- List of reports
- Anti-anxiety effect of Acanthopanax senticosus through autonomic nerve regulation
Anti-anxiety effect of Acanthopanax senticosus through autonomic nerve regulation
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Anti-anxiety effect of Acanthopanax senticosus
through autonomic nerve regulation
Presented at the 135th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (2015)
- Study Objectives
- When excessively stressful conditions persist, the action of autonomic nerves (the balance between the activities of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves) becomes disturbed, causing physical and mental disorders. Acanthopanax senticosus (AS) is reported to have a regulatory action on the autonomic nervous system. However, to date, there have been a small number of evidences of this claim from scientific study. Accordingly, the autonomic nerve regulating action of AS was tested using anxiety stress model rats.
- Study method
- After 1 week of acclimatization, a bioelectric potential transmitter was attached to each of a group of 6-week-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) strain male rats to investigate the action of autonomic nerves (the balance between the activities of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves). The rats in the AS group were allowed free access to food compounded with 5% AS extract for a week. On the day of the test, the rats were placed on the edge of elevated bridge (180 cm high; an approximately 5-cm-wide bridge with no wall on either side) for height stress (fear, anxiety stress) loading, after which the period for which they remained there until they moved to a safe room 110 cm from the edge was determined (0 h). Subsequently, 1 mL of 5% AS extract solution was orally administered to the rats, and the time they remained on the elevated bridge (open arm) was determined at 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 h by the same method. The autonomic nerve activity was also investigated at the same time.
- Results
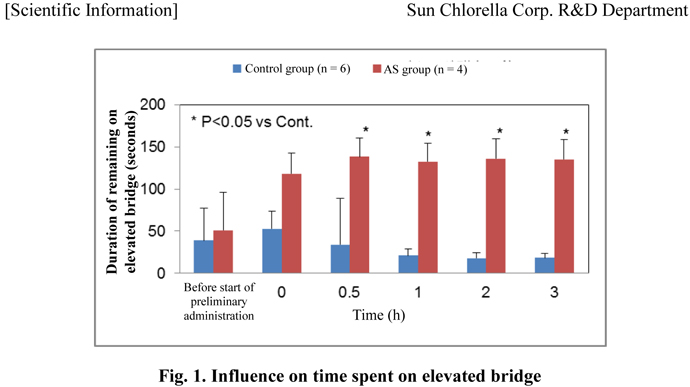
- Rats placed on the elevated bridge experienced fear and anxiety and immediately moved into a
safe room installed on the elevated bridge. However, the period before moving to the safe room
after 0.5 h was significantly prolonged in the AS group compared with the control group (Fig.
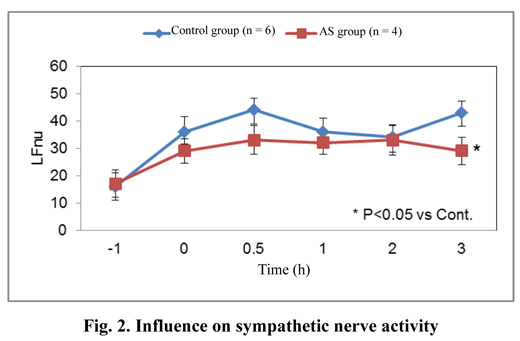
1). Although HFnu*, an index of parasympathetic nerve activity, was not influenced, LFnu*, an
index of sympathetic nerve activity, was significantly decreased in the AS group at 3 h (Fig. 2).
Among the autonomic nerve activities, the activity of sympathetic nerves was enhanced in rats
that experienced fear and anxiety, but AS was found to suppress such enhancement.
These result suggests that ingestion of Acanthopanax senticosus may build up resistance to fear and anxiety stress by regulating the action of autonomic nerves, particularly that of sympathetic nerves.
Terminology
- * Indices of autonomic nerve activities
- LFnu, an index of sympathetic nerve activity, and HFnu, an index of parasympathetic nerve activity, obtained from electrocardiograph frequency analysis.
Details
- Academic society:
- The 135th Annual Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (2015)
- Title:
- The induction of anti-anxiety action by the autonomic nerve functional regulation of Acanthopanax senticosus
- Authors:
- Wataru Nishiguchi1), Chiaki Kusukami1), Shoko Narai1)
, Momoko Ishino1),
Hirotaka Oikawa1), Miwa Nakagawa1), Hideo Takekoshi2),
Masako Hoshizaki2), Sachiyo Nakao3), Takahiko Fujikawa1,3) - Affiliation:
- 1. Department of Pharmacy, Suzuka University of Medical Science
2. Sun Chlorella corp. 3. Mie University Graduate School of Medicine





