- TOP
- List of reports
- An investigation of the mechanism of a (1・6)-β-D-glucan protein complex purified from the fruiting
bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill (Himematsutake) to inhibit the growth of lung tumors and angiogenesis in the tumors
An investigation of the mechanism of a (1・6)-β-D-glucan protein complex purified from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill (Himematsutake) to inhibit the growth of lung tumors and angiogenesis in the tumors
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
An investigation of the mechanism of a (1・6)-β-D-glucan protein complex
purified from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill (Himematsutake) to inhibit the growth of lung tumors and angiogenesis in the tumors
Published in Medicine and Biology
- Objectives
- Agaricus blazei Murill (Himematsutake) is known to have a polysaccharide, (1→6)-β-D-glucan protein complex (hereafter, "ABP"), which exerts its antitumor effect by enhancing the immune system. However, there are still unknown factors about the mechanism of the antitumor effect. Thus, we conducted studies in mice to clarify the effects of ABP ingestion on the growth and metastasis of lung tumors as well as their ability to form blood vessels that deliver nutrients to the tumor cells.
- Methods
- ABP was administered to mice, in which lung tumor cells were implanted in the thigh, at doses of 10, 50, and 100 mg/kg for 21 days to assess the growth of lung tumors and the number of metastases. In addition, ABP was administered to mice, in which the same lung tumor cells were implanted into the back, at doses of 20 and 100 mg/kg for 15 days to assess its effect on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). It should be also noted that ABP was orally administered twice daily in the morning and evening.
- Results
- Administration of ABP was shown to inhibit the growth and metastasis of lung tumors (Figs. 1 and 2). In addition, the inhibitory effect of ABP on VEGF was demonstrated to contribute to the mechanism of the antitumor effect (Fig. 3). Furthermore, the higher the ABP concentration is, the stronger the antitumor and inhibitory effects.
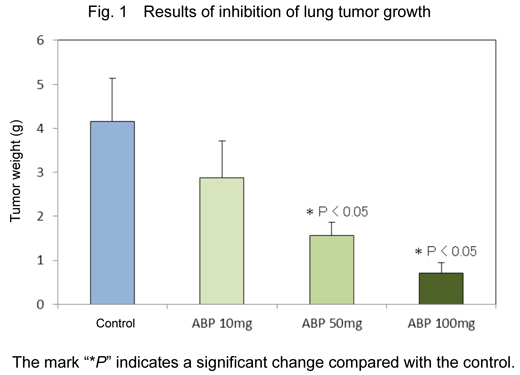
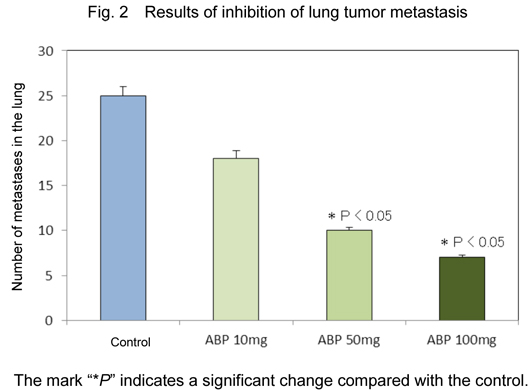
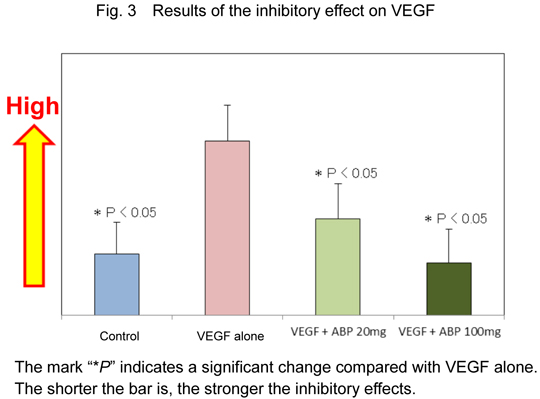
This is the first report demonstrating that ABP ingested inhibits the growth and metastasis of lung tumors as well as the ability of the tumor cells to form blood vessels.
Details
- Journal:
- Medicine and Biology. 2012; 156(2):53-61
- Title:
- Inhibitory Actions of a (16)-β-D-Glucan Purified from the Fruiting Bodies of Agaricus blazei Murrill (Himematsutake) on Lung Metastasis and Angiogenesis
- Authors:
- Hiroko Ito1), Masaki Fujishima2), Yukari Arakawa2), Fukuyoshi Nakata3), and Hitoshi Ito4)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Laboratory of Marine Biochemistry, Faculty of Bioresources, Mie University,
2) Sun Chlorella Corp., 3) Power Full Health Foods Corp.,
4) Research Institute of Mycology and Pharmacology





