- TOP
- List of reports
- Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus on behavior and autonomic nerve activity under cohabitation
of different individuals
Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus on behavior and autonomic nerve activity under cohabitation of different individuals
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus on behavior and autonomic nerve activity under cohabitation of different individuals
Presented at the 136th Annual meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (2016)
- Objectives
- The function of the autonomic nerve (balance between the sympathetic nerve and the parasympathetic nerve) is disordered under prolonged overstress, and that may lead to disorder of a body and mind. We have reported that Acanthopanax senticosus affected the autonomic control in an anxious rat model under height stress at the last year's meeting. This time, we inspected the effects of Acanthopanax senticosus on autonomic control in an anxious status at cohabitation of different individuals under a new environment.
- Methods
- To investigate the function of the autonomic nerve (activities of the sympathetic nerve and the parasympathetic nerve), 6-week-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) male rats were attached with a biopotential transmitter and Acanthopanax senticosus group rats were given 1-week free-feeding of 5% Acanthopanax senticosus extract mixed feed after 1-week preliminary breeding. The control rats were given water and basic feed. On the test day, a separately bred control rat and an Acanthopanax senticosus group rat were orally administered with 1 mL of water and that of 5% Acanthopanax senticosus extract water solution, respectively. After that, the 2 rats were cohabited in a new breeding cage (a new environment) for 3 hours. The function of the autonomic nerve was investigated at 1 hour before cohabitation and just after cohabitation (0 hour) as well as 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 hours after cohabitation.
- Results
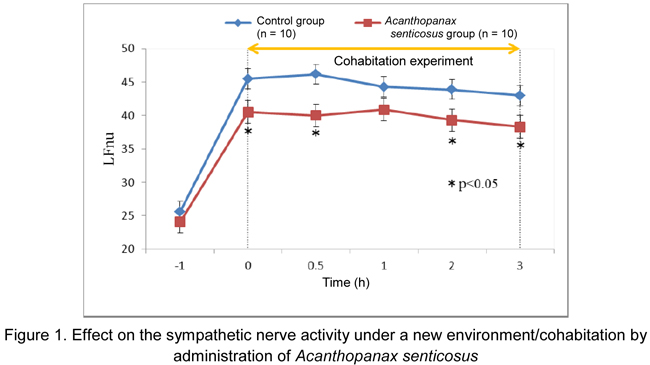
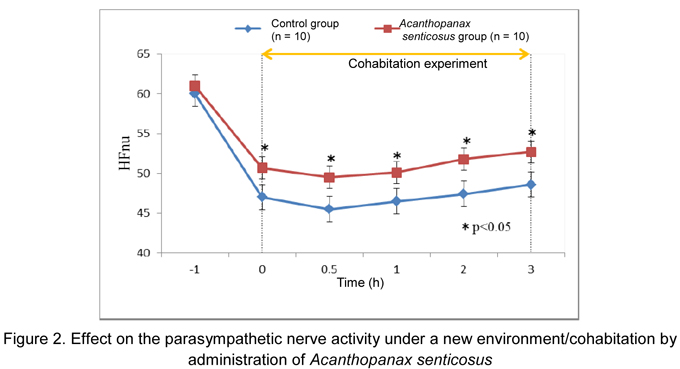
- Cohabitation of different individuals under a new environment is a big stress for rats. In the control
rats, the sympathetic nerve activity was facilitated and the parasympathetic nerve activity was
reduced under the stressed environment. In contrast to the control group, facilitation of LFnu* that
is an index of sympathetic nerve activity was significantly suppressed and reduction of HFnu* that
is an index of the parasympathetic nerve activity was also significantly suppressed in the
Acanthopanax senticosus group from just after cohabitation to 3 hours after cohabitation (Fig.1, 2).
Induction of anxiety and tension by 3-hour cohabitation with unfamiliar rat in a new environment
was also seen from the changes in the functions of the autonomic nerve. Although activity of the
sympathetic nerve out of the autonomic nerve was facilitated in rats that felt anxiety and tension,
Acanthopanax senticosus inhibited the facilitation and further inhibited reduction in the
parasympathetic nerve activity.
Based on the above results, Acanthopanax senticosus was suggested to be a useful food that may increase adaptability to the stress associated with anxiety and tension in a new environment or interpersonal relations by regulating the autonomic nervous balance.
Terminology
- *LFnu
- An index of the sympathetic nerve activity from the frequency analysis of an electrocardiogram
- *HFnu
- An index of the parasympathetic nerve activity from the frequency analysis of an electrocardiogram
Details
- Meeting:
- 136th Annual meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (2016)
- Title:
- Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus on behavior and autonomic nerve activity under cohabitation of different individuals
- Authors:
- Shohei Miyazaki1 , Daisuke Beppu1 , Noriko Hayashi1 , Hirotaka Oikawa1 , Miwa Nakagawa1 , Hideo Takekoshi2 , Masako Hoshizaki2 , Sachiyo Nakao3 , Takahiko Fujikawa1,3
- Affiliation:
- 1 Suzuka University of Medical Science, Department of Pharmaceutical
Sciences;
2 Sun Chlorella Corporation; 3 Mie University, Faculty of Medicine





