- TOP
- List of reports
- Exploration of active ingredients that contribute to health function of Chlorella
Exploration of active ingredients that contribute to health function of Chlorella
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Exploration of active ingredients that contribute to health function of Chlorella
Presented at the 2016 Annual Conference of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry
- Objectives
- Various kinds of water-soluble ingredients such as proteins are contained in Chlorella, and activities of the immunostimulation and the lipid metabolism improvement are considered to be derived from these ingredients. However, the concrete active ingredients and the mechanism of action still remain unclear. The present study was conducted to explore active ingredients related to activities of the immunostimulation or the lipid metabolism improvement in the water-soluble ingredients from Chlorella using an assay with cells.
- Methods
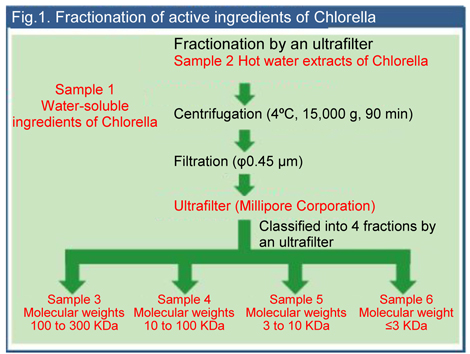
- Water-soluble ingredients of Chlorella were fractionated in 6 fractions (Fig.1) based on the
molecular weight, and activities of the immunostimulation and the lipid metabolism improvement
were evaluated for each fraction.
The murine macrophage-like cell line RAW264 was used for the Nitric Oxide (NO) induction assay (immunostimulation activity), and the murine preadipocyte 3T3-L1 cells were used for the fat accumulation inhibitory test (lipid metabolism improvement activity).
- Results
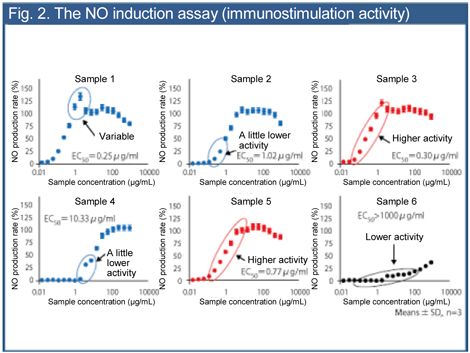
- [NO induction assay]
The NO induction activity (immunostimulation activity) was confirmed in the fraction with molecular weights of 100,000 to 300,000 (sample 3) and the fraction with molecular weights of 3,000 to 10,000 (sample 5) (Fig.2).
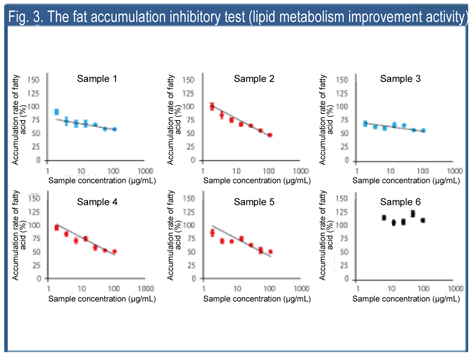
[Fat accumulation inhibitory test]
The fat accumulation inhibitory activity (lipid metabolism improvement activity) was confirmed in hot water extracts of Chlorella (sample 2), the fraction with molecular weights of 10,000 to 100,000 (sample 4), and the fraction with molecular weights of 3,000 to 10,000 (sample 5) (Fig.3). - Based on the above results, ingredients in the fraction with molecular weights of 3,000 to 10,000
(sample 5) was suggested to be involved with the immunostimulation activity and the lipid
metabolism improvement activity.
We will further explore the active ingredient by narrowing the fractions and evaluate the mechanism of action with changes in gene expression by a microarray analysis.
Details
- Meeting:
- The 2016 Annual Conference of the Japan Society for Bioscience,
Biotechnology and Agrochemistry - Title:
- Exploration of active ingredients that contribute to health function of Chlorella
- Authors:
- Tatsuya Iseki1) , Junya Ito1), Oki Higuchi2), Masato Sasaki2) , Satoru Horigome3) , Akio Watanabe3), Hideo Takekoshi4), Masaki Fujishima4), Masato Onishi4) , Kiyotaka Nakagawa1), Teruo Miyazawa5,6)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Food and Biodynamic Chemistry Laboratory, Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University; 2) Biodynamic Plant Institute Co.,Ltd.; 3) Japan Food Research Laboratories; 4) Sun Chlorella Corporation; 5) New Industry Creation Hatchery Center, Tohoku University; 6) Food and Health Science Research Unit, Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University





