- TOP
- List of reports
- Effects of Combination of Chlorella Intake and Short-Term High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise
on Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise Capacity
Effects of Combination of Chlorella Intake and Short-Term High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise on Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise Capacity
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Effects of Combination of Chlorella Intake and Short-Term High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise on Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise Capacity
Presented at the 71st Annual Meeting of Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science
- Study objectives
- The tests on animals and human beings show that continuous chlorella intake has effects of improving aerobic exercise capacity. Also, in the animal tests, 6-week of short-term high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT, Tabata training) was reported to enhance both aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity. However, it is unknown whether the combination of chlorella intake and HIIT has effects on anaerobic and aerobic exercise capacity in human beings. Thus, we examined the effects of the combination of chlorella intake and HIIT on anaerobic and aerobic exercise capacity in human beings.
- Study method
- A double-blind crossover study was conducted in 6 healthy young males without
exercise habits (age: 21±1 years, height: 170±3 cm, body weight: 63±4 kg), comprising
one test with chlorella intake and another with placebo intake during a 3-week HIIT
intervention period with a 5-week interval between tests.
An all-out HIIT protocol comprises 7-8 sets of 20-second bicycle ergometer exercise at an intensity of 170% maximum oxygen uptake*1 followed by 10 seconds of rest 3 times a week. During the HIIT intervention, the subjects received 20 tablets (4g) of chlorella or placebo a day. (They received 10 tablets twice a day after breakfast and dinner.) Before and after the intervention, maximum oxygen uptake was measured to evaluate aerobic exercise capacity and maximum oxygen deficit*2 was measured to evaluate anaerobic exercise capacity.
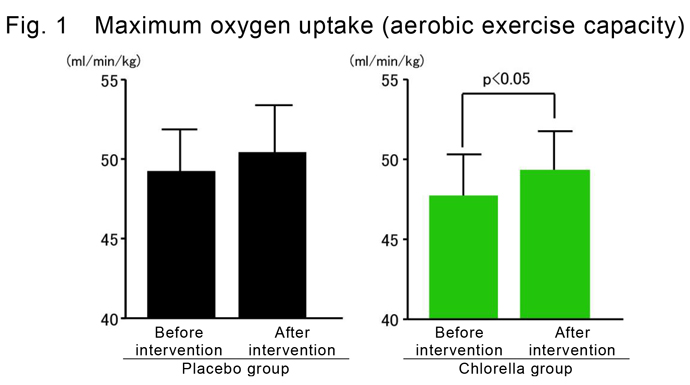
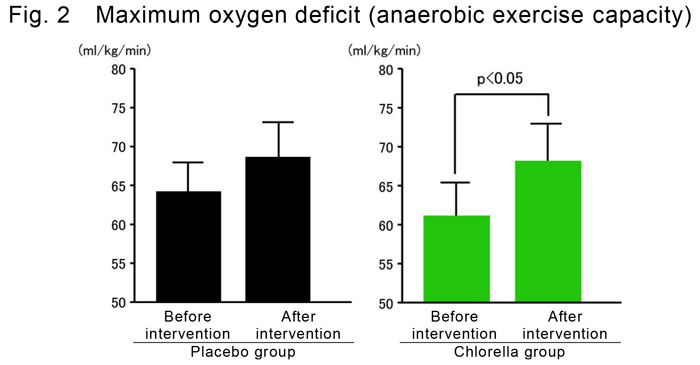
- Results
- When the subjects received chlorella with 3-week HIIT, maximum oxygen uptake and
maximum oxygen deficit significantly increased after the intervention (P<0.05). In
contrast, no significant difference was observed in the subjects receiving placebo with
HIIT before and after the intervention (Figs. 1 and 2).
The above results suggested that chlorella intake with short-term HIIT could efficiently improve both anaerobic and aerobic exercise capacity compared with HIIT alone.
Terminology
- *1: Maximum oxygen uptake
- Physical fitness index of aerobic exercise capacity It is a “maximum volume of oxygen consumed by the body per unit time (and body weight)”. The larger value means better whole-body endurance.
- *2: Maximum oxygen deficit
- Physical fitness index of anaerobic exercise capacity Oxygen uptake increases at the start of exercise, but a difference occurs between oxygen demand and oxygen uptake in the initial stage of exercise. The difference is called oxygen deficit, which is thought to be supplied by the anaerobic energy supply system other than the aerobic energy supply system. The larger value means better anaerobic exercise capacity.
Details
- Academic society:
- The 71st Annual Meeting of Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science
- Title:
- Effects of Combination of Chlorella Intake and Short-Term High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise on Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise Capacity
- Authors:
- Moe Oshiden1), Shumpei Fujie1),2), Natsuki Hasegawa1),2),Naoki Horii1), Katsunori Machi1), Jo Uchu1), Toru Mizoguchi3),Masato Onishi3), Izumi Tabata1), Motoyuki Iemitsu1)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Ritsumeikan University Graduate School
2) Research Fellowship for Young Scientists (DC) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
3) Sun Chlorella Corporation





