- TOP
- List of reports
- Preventive effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa administered orally on carbon tetrachloride-induced
experimental liver injury in rats
Preventive effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa administered orally on carbon tetrachloride-induced experimental liver injury in rats
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Preventive effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa administered orally on carbon tetrachloride-induced experimental liver injury in rats
This study was published in the scientific journal “Japanese Pharmacology & Therapeutics Vol. 47 No. 7”.
- Objective
- The preventive effects of chlorella on liver injury have been already reported in Preventive effect of Chlorella pyrenoidosa on hepatic injury in rats. In the present study, the improving effects of chlorella were evaluated with a rat model of carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4)*1-induced liver injury.
- Methods
- For preparation of rat liver injury model, 25% olive oil solution of CCl 4 was injected
subcutaneously into rats once daily at 1.0 mL/kg (0.25 mL/kg as CCl 4) for 4 day s. This
study was performed by preparing the following 4 experimental groups consisting of 5 rats
each: control group (subcutaneous injection of olive oil alone); control group treated with
CCl4 (subcutaneous injection of CCl4 at 0.25 mL/kg); group treated with CCl4 + oral
administration of chlorella at 300 mg/kg/day; and group treated with CCl 4 + oral
administration of chlorella at 1,200 mg/kg/day.
According to the experimental schedule shown in Figure 1, chlorella was orally administered for 4 consecutive days before and after initiating subcutaneous injections of CCl4, and GOT, GPT, lipid peroxides, and triglycerides were then measured and evaluated 24 hours after the final administration of chlorella.
- Results
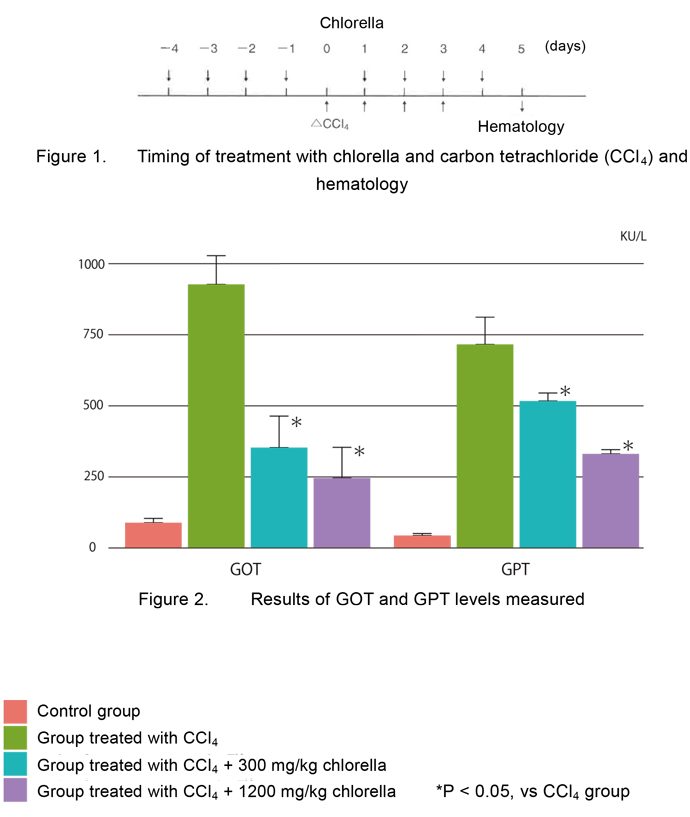
- Figure 2 shows the effects of chlorella on GOT and GPT levels in rats with liver injury
caused by CCl4.
CCl4-induced increases in GOT and GPT levels were significantly inhibited by oral administration of chlorella at doses of 300 and 1,200 mg/kg/day.
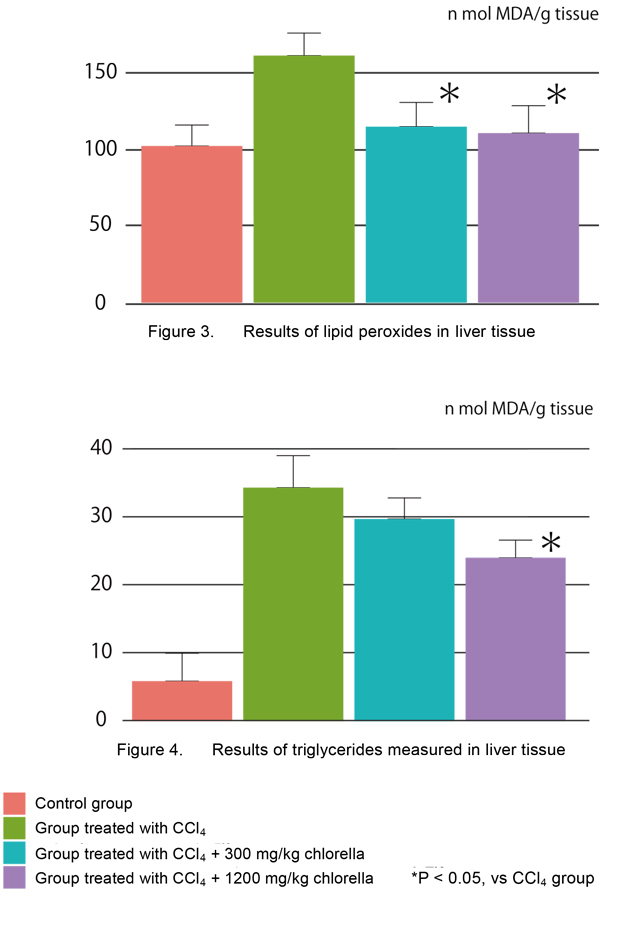
Figure 3 shows the effect of chlorella on lipid peroxides in liver tissue of rats with liver injury caused by CCl4. Lipid peroxides were measured by malondialdehyde (MDA) generated by the thiobarbituric acid-based method of Buege and Aust.
The data are not shown in this report, but no changes in serum lipid peroxides were noted after subcutaneous injections of CCl4 or oral administration of chlorella. In contrast, the level of lipid peroxides in liver tissue was significantly increased by injections of CCl4 and significantly reduced to the level of control group by oral administration of chlorella.
Figure 4 shows the effect of chlorella on triglycerides in liver tissue of rats with liver injury
caused by CCl4. The data are not shown in this report, but the level of serum triglycerides was significantly reduced by injections of CCl4 and the reduction was rarely improved by oral administration of chlorella. In contrast, the level of triglycerides in liver tissue was significantly increased by injections of CCl4 and the increase was significantly inhibited by oral administration of chlorella at 1,200 mg/kg/day.
These results indicated that chlorella significantly inhibited GOT and GPT levels, which are generally increased in liver injury, and also inhibited the increases in lipid peroxides and triglycerides in liver tissue.
Terminology
- *1: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
- This compound has very strong hepatotoxicity and has been shown to induce hepatocellular carcinoma in animal studies with mice and rats.
Details
- Publication:
- Japanese Pharmacology & Therapeutics (monthly) Vol. 47, No. 7 issued on July 20, 2019
- Title:
- Preventive effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorophyceae) of oral administration on carbon tetrachloride in experimentally induced liver injury of rats
- Authors:
- Hiroko Ito1), Masaki Fujishima2), Eri Okumura2), Fukuyosi Nakada3), and Hitoshi Ito4)
- Affiliation:
- 1) Laboratory of Marine Biochemistry, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie
University
2) Production and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
3) Powerful Health Foods Corporation
4) Research Institute of Mycology and Pharmacology





