- TOP
- List of reports
- Water extract of chlorella and Phenethylamine a functional ingredient in Chlorella significantly
mitigated high fat diet (HFD) induced liver damage.
Water extract of chlorella and Phenethylamine a functional ingredient in Chlorella significantly mitigated high fat diet (HFD) induced liver damage.
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
Water extract of chlorella and Phenethylamine a functional ingredient in Chlorella significantly mitigated high fat diet (HFD) induced liver damage.
Published in the journal of npj science of food
- Research objectives
- Previously Sun Chlorella had identified phenethylamine (PHA) which is classified as
monoamine in the hot water extract of chlorella pyrenoidosa(WEC) as functional factor that
expands the life span of superoxide dismutase 1 gene(Sod1) mutant adult of Drosop hila
melanogaster. However, the biological activity of trace amounts of PHA has not been
examined in mammals. We continued our collaboration with Kyoto University aiming to
elucidate the mechanism of action with PHA.WEC related on mitigation of high fat d iet
induced hepatic damages rats model with non alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD), in
which oxidize of lipids accumulated in the liver by consuming a high fat diet leads to
disease progression.
The article can be viewed freely. For more details, check the article. (Link)
- Test method
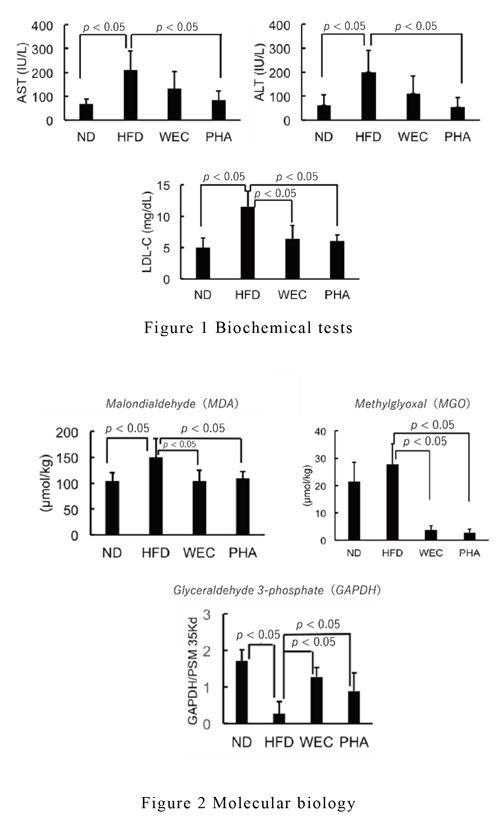
- NAFLD model mice fed a 60% high-fat diet were orally administered chlorella water extract at 100 mg/kg (WEC group) or phenethylamine at 10 μg/kg (PHA group) for 12 weeks. Evaluations included biochemical tests in the blood and molecular biology tests in the liver, and the results were compared with mice kept on normal diet (ND group) and 60% high-fat diet (HFD group) only. Significant variation was assessed at p < 0.05.
- Results
Biochemical tests
AST and ALT, which are indicators of liver damage, were significantly lower in the WEC and PHA groups than in the HFD group, indicating an inhibition of elevation in the PHA group. In addition, LDL cholesterol was significantly suppressed in the WEC and PHA groups, which was comparable to that in the ND group. (Figure 1)
Molecular biology test
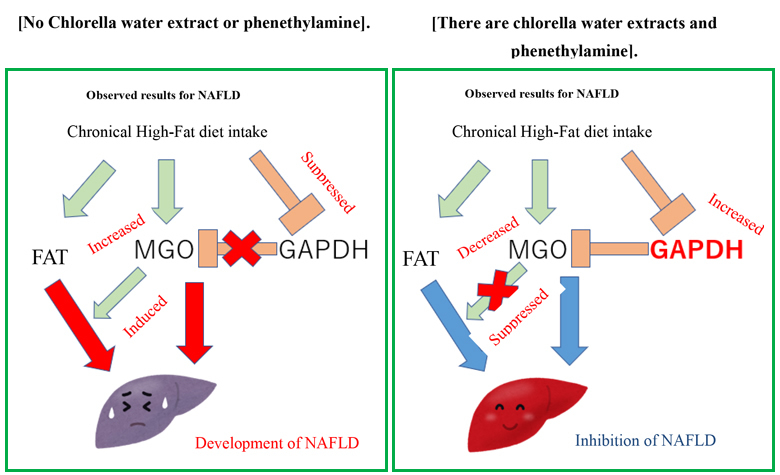
Oxidation of lipids in the liver produced ma londialdehyde (MDA), an indicator of oxidative stress and highly cytotoxic, inhibited the increase in the WEC and PHA groups compared with the HFD group, showing values comparable to those in the ND group. Therefore, methylglyoxal (MGO), which promotes MDA oxidize and is cytotoxic, was Study-report Sun Chlorella Study Site http ://lab.sunchlorella.com/link measured from lipids and showed a significant decrease in the WEC and PHA groups. measured from lipids and showed a significant decrease in the WEC and PHA groups. Accordingly, we measured the levels of glyceraldehydeAccordingly, we measured the levels of glyceraldehyde--3 phosphate dehydrogenase 3 phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), which may reduce the levels of precursors of MGO and m(GAPDH), which may reduce the levels of precursors of MGO and maintain the aintain the antioxidant capacity of fatty liver, and found that the HFD group had a greater reduction antioxidant capacity of fatty liver, and found that the HFD group had a greater reduction compared with the ND group, whereas the WEC and PHA groups had a reversal. (Figure compared with the ND group, whereas the WEC and PHA groups had a reversal. (Figure 2)- Thus, "Chlorella aqueous extract or phenethylamine restores GAPDH level and consequently inhibits the production of MGOs and MDAs in liver injury induced by high fat diet" was elucidated as the mechanism of action.
Details
- journal:
- npj Science of Food
- Title:
- Phenethylamine in chlorella alleviates high fat diet induced mouse liver damage by regulating generation of methylglyoxal.
- Authors:
- Yifeng Zheng1), Agustin Martin-Morales1), Jing Wang1), Masaki Fujishima2),
Eri Okumura2) & Kenji Sato1) - Affiliation:
- 1) Division of Applied Biosciences, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University
2) Sun Chlorella Corp.





