- TOP
- List of reports
- The anti-inflammatory activity of Chlorella in beagles with skin disorders
The anti-inflammatory activity of Chlorella in beagles with skin disorders
【Scientific information】
Research and Development Department, Sun Chlorella Corporation
The anti-inflammatory activity of Chlorella in beagles with skin disorders
Findings of this study were presented at the Annual Meeting of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry 2008
- Study Objectives
- Inflammation occurs primarily as a biological defense to protect the body from microorganisms. Inflammatory reactions that have become chronic, however, are known to be involved in rheumatic arthritis and other diseases. We have already reported on the finding of our in vitro evaluation test, that Chlorella inhibits the activity of cyclooxygenase-2 and phospholipase A2, which are enzymes involved in the induction of inflammation (Search Chlorella's pharmacological activity). This time, to confirm the effects of Chlorella in vivo, we conducted a study using beagles that had spontaneously developed chronic dermatitis.
- Method of experiments
- Beagles with chronic dermatitis were divided into two groups (5 dogs per group), and were given ordinary feed or the one with Chlorella powder (0.1 g/kg of weight/day of Chlorella added) for 4 weeks. Improvement of dermatitis was evaluated by a veterinarian on a daily basis, and by a blood test performed at the end of the study.
- Results
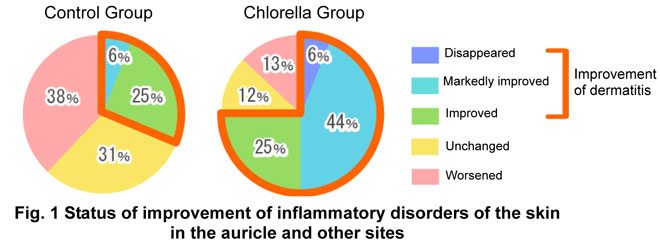
- After four-week intake of feed, 6% of the dogs in the Chlorella Group
exhibited disappearance of inflammation in the auricle and other affected areas,
while 75% exhibited "improvement of dermatitis", including those of which
condition was judged to be "markedly improved" or "improved". On the other
hand, none of the dogs in the Control Group exhibited disappearance of
inflammation; 31% exhibited "improvement of dermatitis" but 38% exhibited
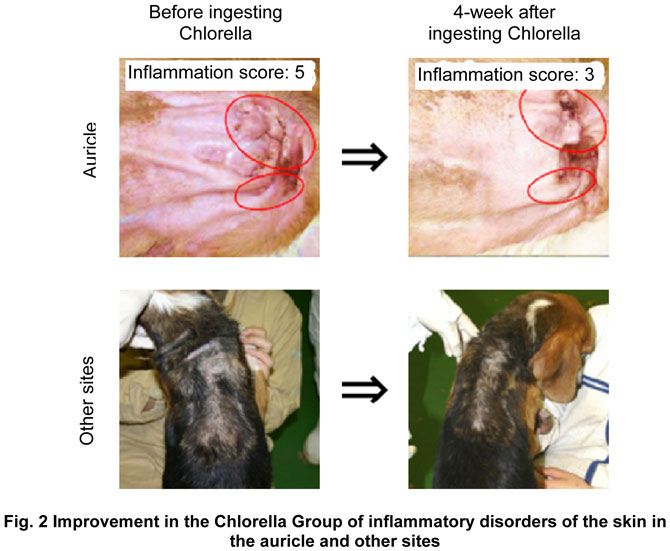
aggravation of it (Fig. 1). The Chlorella Group also exhibited a tendency for
inflammation score, an indicator of the degree of inflammation, to decrease (Fig. 2).
In the blood test, moreover, they exhibited a significant decrease in neutrophil
count, which increases during inflammation.
The results of this study suggest that Chlorella is effective in improving inflammation in vivo as well as in vitro.
Presented at a scientific meeting
- Academic society:meeting
- The Annual Meeting of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology and Agrochemistry 2008
- Title:
- Chlorella's anti-inflammatory activity in beagles with skin disorders
- Authors:
- Morihiko Maeda, Yoshie Kasuya, Kazuyuki Yuasa, Takashi Hiranaka, Hirofumi Chubachi1), Masako Saito2), Hideo Takegoshi2)
- Affiliation:
- NALC,1) Hokkaido Medical Plant Research Institute,2) Sun Chlorella Corporation





